Chapter 8 More Functions and Identities
- \(\displaystyle \blert{\textbf{Sum and Difference Formulas}}\)
- \(\displaystyle \blert{\textbf{Inverse Trigonometric Functions}}\)
- \(\displaystyle \blert{\textbf{The Reciprocal Functions}}\)
Mapmakers have always faced an unavoidable challenge: It is impossible to translate the surface of a sphere onto a flat map without some form of distortion. Over the years, a variety of map projections have been developed to suit different uses.
The sixteenth century was an age of discovery, when explorers and merchants began sailing to distant and previously unknown lands. But at that time there was no reliable technology for navigation. Although more regions of the world were being mapped more accurately, a flat map by itself was not enough to help a sailor in the middle of the ocean.
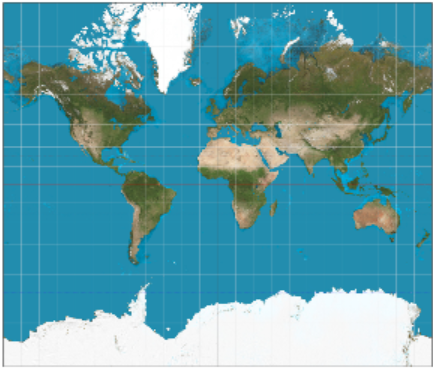
In 1569, the Flemish cartographer Gerardus Mercator published a new map using what is known as a cylindrical projection. To imagine how a Mercator projection works, picture shining a light through a glass globe onto a piece of paper rolled into a cylinder and wrapped around the globe. The cylinder is tangent to the globe at its equator.
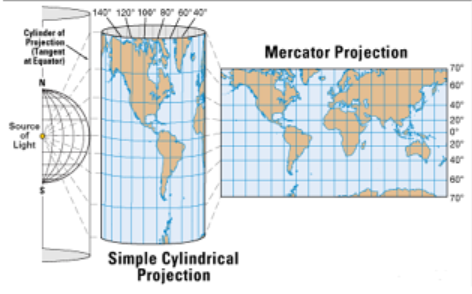
Notice how the latitude lines are farther apart the farther you get from the Equator. This projection distorts the size of objects as the latitude increases, so that Greenland and Antarctica appear much larger than they actually are.
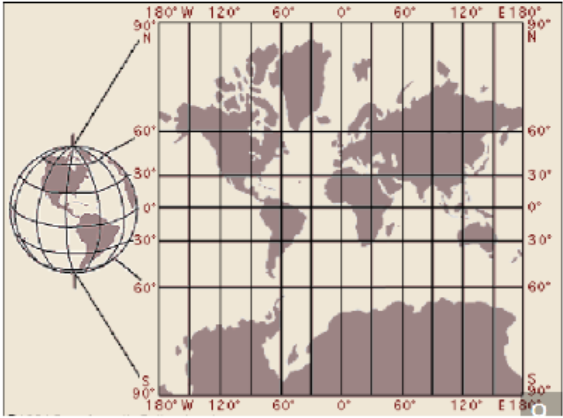
But the Mercator projection map is ideally suited for navigation, because any straight line on the map is a line of constant true bearing. If a navigator measures the bearing on the map from his location to his destination, he can set his ship’s compass for the same bearing and maintain that course.
However, the Mercator projection does not preserve distances. On a globe, circles of latitude (also known as parallels) get smaller as they move away from the Equator towards the poles. Thus, in the Mercator projection, when a globe is "unwrapped" on to a rectangular map, the parallels need to be stretched to the length of the Equator. Mercator had to increase the scale of his map gradually as it moved away from the equator, so that the latitude lines appear equal in length to the equator.
The horizontal scale factor at any latitude must be inversely proportional to lengths on that latitude. Because the radius of the circle of latitude \(\theta\) is \(R \cos \theta\text{,}\) the corresponding parallel on the map must be stretched by a factor of \(\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta}\text{.}\) And because the secant is the reciprocal of the cosine, the scale factor is proportional to the secant of the latitude.
A variety of "equal area" projections have been developed in modern times, but the Mercator projection is still widely used, in classrooms and atlases. For many people, it represents our image of the world.